CSS Positions
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
Default mode-CSS position of an element is static.
- New Position Context gets created whenever position property is other than static for that element .
- top/bottom/left/right/z-index can be applied to that element.
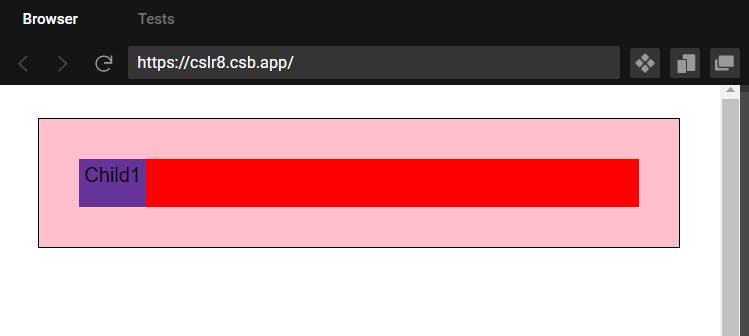
1)Position-Relative
- Element will be displaced according to itself and it's current position.
- Will look like as static until applied with other properties like top/bottom etc.
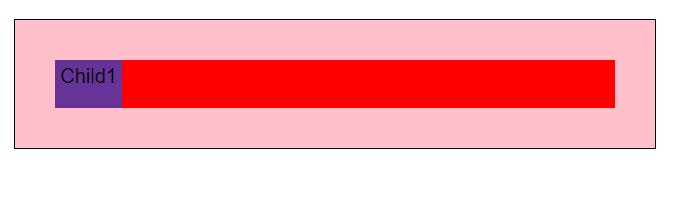
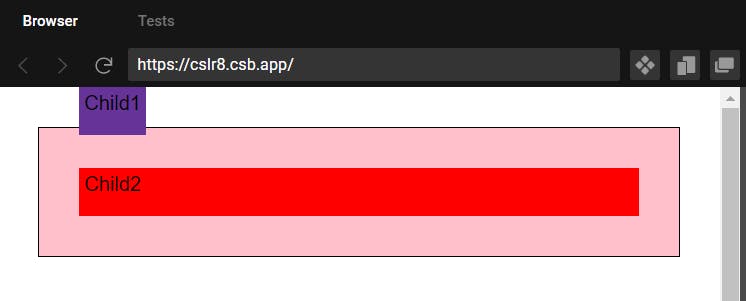
2)Position-Absolute
HTML
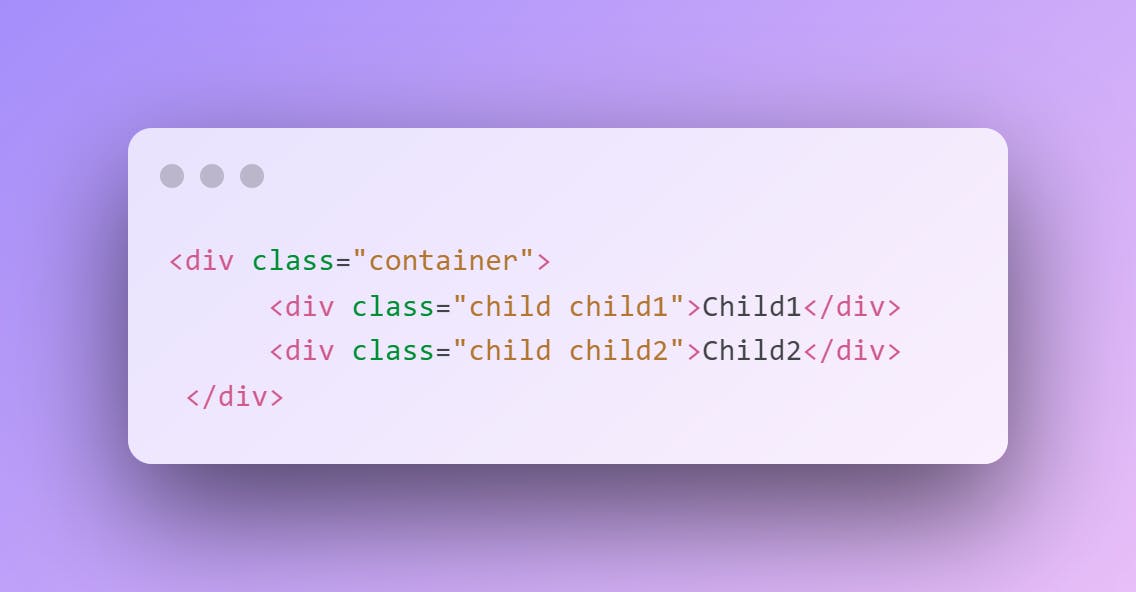
CSS
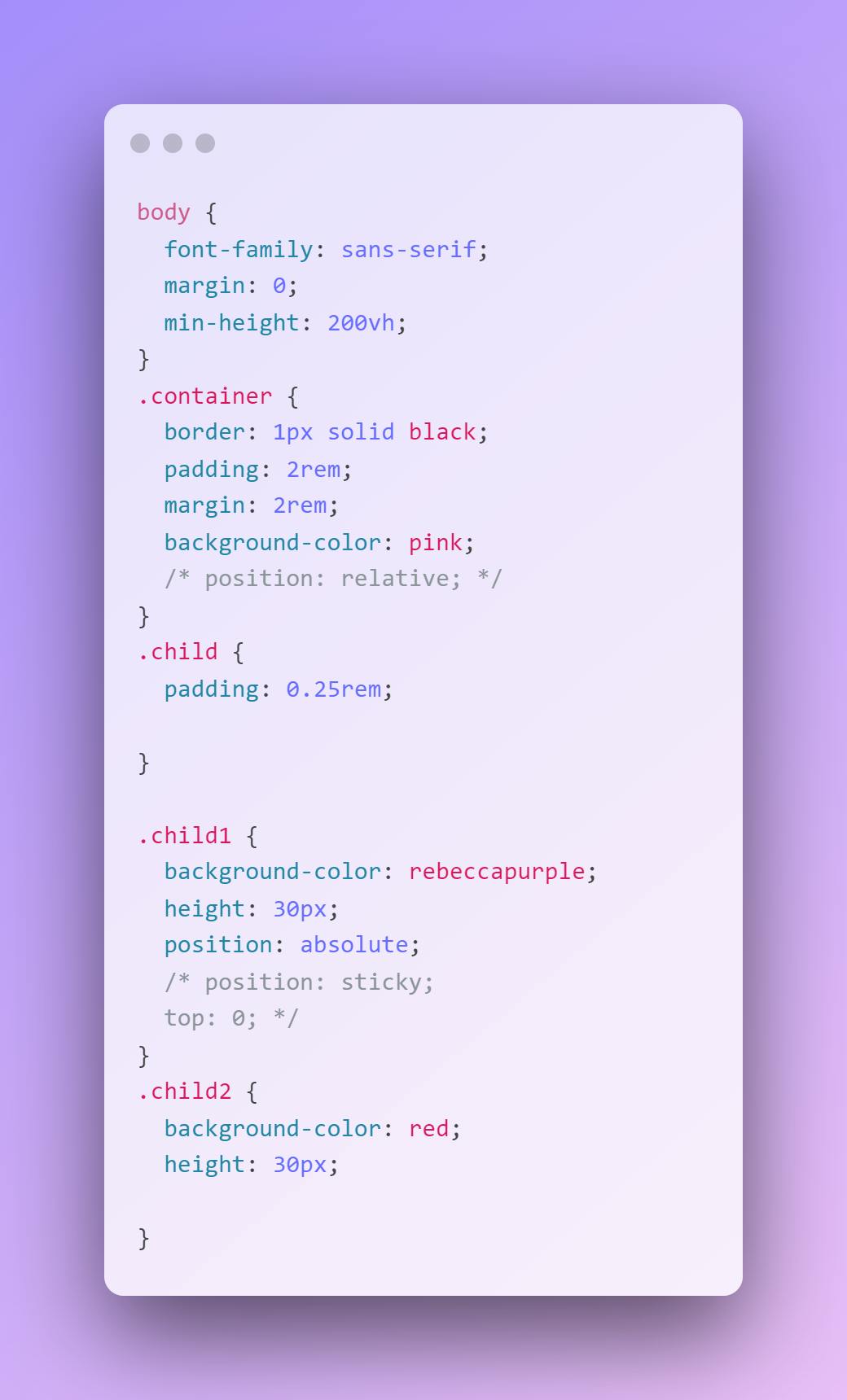
Output
- So absolute removes the element from the document flow and other elements if any below will take it's position.
- Positions according to first no-static parent, if none would fallback to html. -Element will have a new position context created relative to parent.
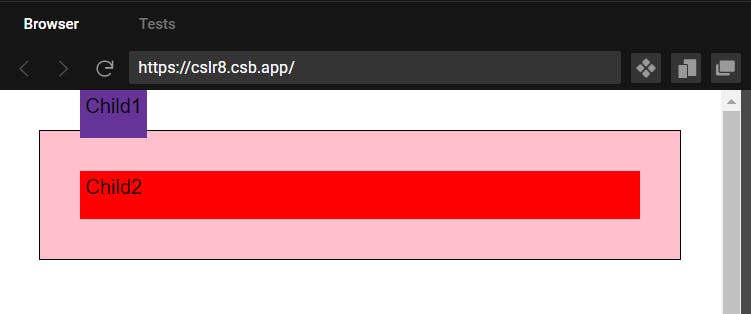
Output when child 1 with absolute given top 0
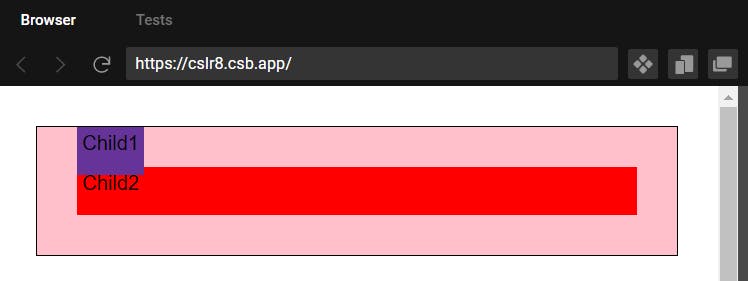
Output when container is given position relative on top of previous state.
3)Fixed
Output State 1
.child1 {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
height: 30px;
position:fixed;
/* position: sticky; */
/* top:0; */
}
container- static
state 2 (uncommenting top 0)
-Fixed is like normal absolute -It positions relative to screen size, not relative to parent -Element will be forever fixed at that position.
4)Sticky
-state1
.child1 {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
height: 30px;
/* position: fixed; */
position: sticky;
/* top: 0; */
}
Element will behave as normal relative and there will be no changes until top/bottom specified.
state 2
.child1 {
background-color: rebeccapurple;
height: 30px;
position: sticky;
top: 0;
}
Element will stay on top until it slides through all the elements below it in that parent container.
Thank you for reading :)